tutorial: RoboVM and dependent watchOS app
20 May 2020 | tutorial watchosDISCLAIMER: its not possible to create watchOS application with RoboVM. This tutorial describes how embed one created in Xcode as companion to RoboVM iOS application.
To package watchOS app RoboVM was adapted to handle packaging, signing and launching (on a simulator).
Code: experimental code was pushed to dkimitsa/watchkit-support branch.
(skip long read and start embedding watchOS app)
Changes to RoboVM
Packaging
Xcode produces watch.app and it has to be copied into ios.app/Watch/watch.app directory. Following lines in robovm.xml tells RoboVM to look for watch.app and embed it:
<watchKitApp>
<app>watch.app</app>
<!-- <extensions>
<extension profile="C87CF3BF-1B73-4E32-9CCB-71C3D6AE7E8E">watch Extension</extension>
custom signing if of watch.app extensions
might be done here if required
</extensions>-->
</watchKitApp>
<appExtensionPaths>
<!-- path where app extensions (such as watch.app) will be searched in -->
<path>exts</path>
</appExtensionPaths>
Both <app> and extension keys are actually app extensions tags and support its signing customization.
<app> tag specifies the name of watchOS application to be copied. RoboVM will look for it among <appExtensionPaths>.
Code signing
Signing of dependent watchOS application is similar to signing app extensions. Same rules for bundle ids: each child shall extend Id of parent. Example: if host(iOS) has com.corner.game then watchOS one shall be extended with suffix like this: com.corner.game.$SUFFIX$ (where $SUFFIX$ is some ID string).
Folowing elements will be signed:
- watchOS application;
- watchOS application’s extension(s);
All these will be signed with single certificate used for signing host iOS application. Every of these requires provisioning profile. Either generate one per entry or having wildcard one is a good idea.
Signing of these entries might be customized in robovm.xml:
- watch application by
<watchKitApp><app>; - any watch extension by
<watchKitApp><extensions><extension>.
All these tags have structure of application extension configuration tag.
Application extension tag changed
Application extension tag supports following attribute:
profile– used to specify provisioning profile to be used for signing;
Tag was extended with additional attributes:
skipSigning– if true, re-signing of extension will be skipped and extension will be copied as it is;suffix– to buildbundle idof extension by attaching suffix toparent bundle id.
Support for a watch simulator (Idea plugin)
Idea plugin was extended to deploy to and automatically launch paired watchOS simulator. For every iOS simulator that has a pair adding checkbox is displayed in the run configuration dialog:
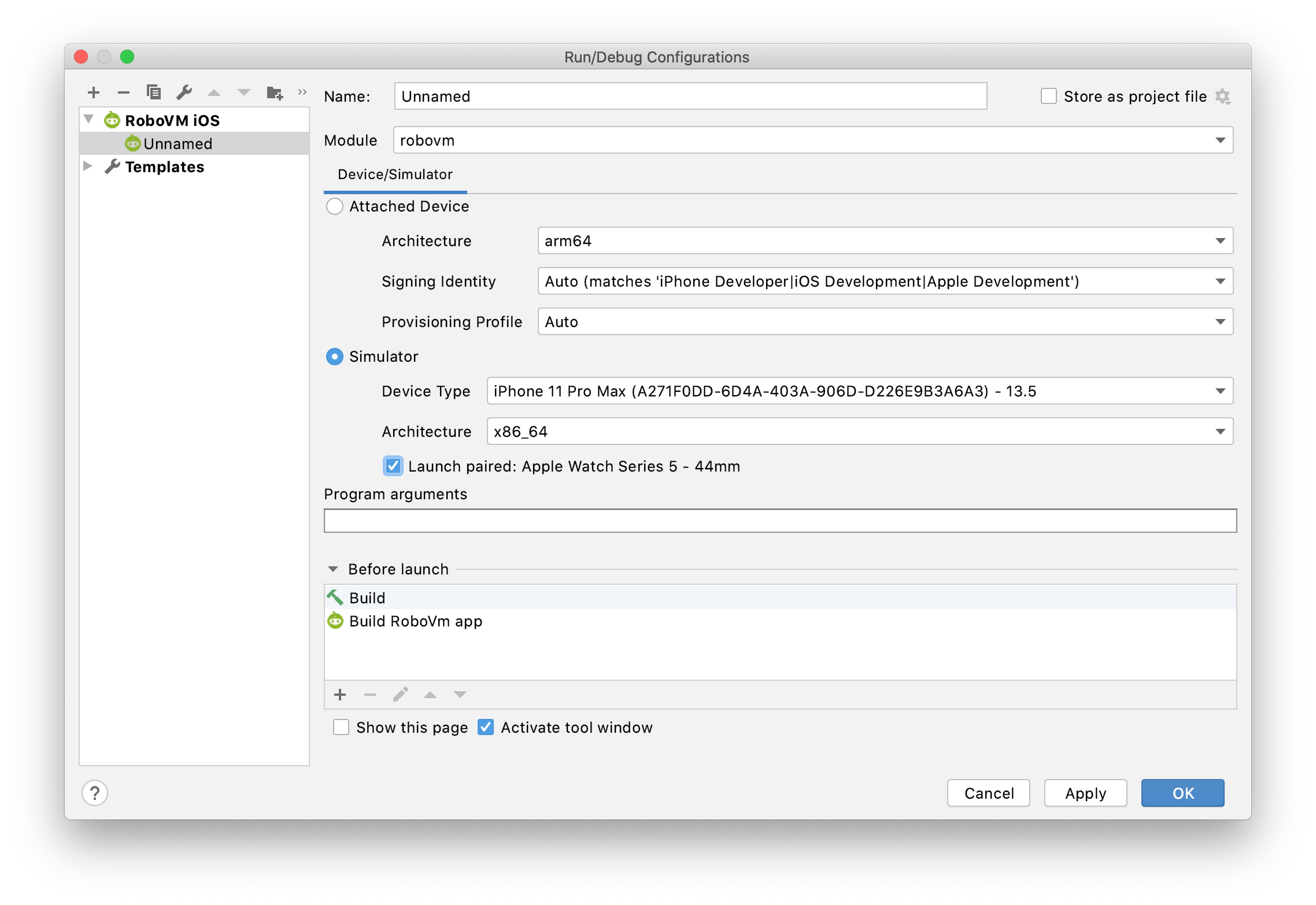
Once checkbox is checked both iOS and paired watchOS simulators will be launched and deployed to.
end of long read
Tutorial: packing simple watchOS app
Source code for this tutorial.
Following will be accomplished during tutorial:
- native swift iOS app using swiftui;
- native watchOS app using swiftui;
- these apps to communicate each other via
WatchConnectivity; - watchOS app will be reused for RoboVM project;
- native swift iOS app will be ported into RoboVM;
- RoboVM app to communicate with native watchOS app via
WatchConnectivity;
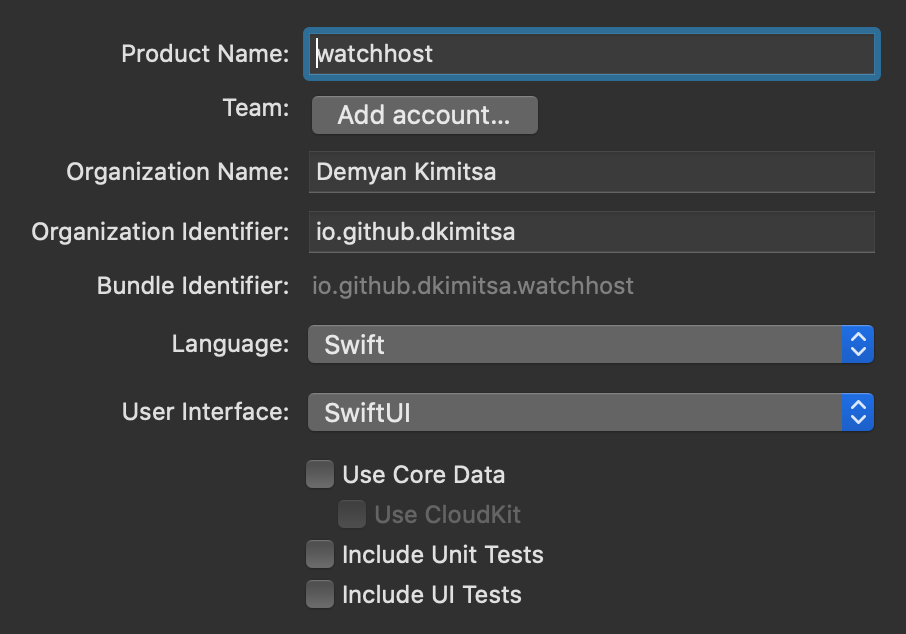
new Xcode iOS (host) project
- Create new
iOS/Single View Appproject; - Select
swiftas language; - Select
swiftuias UI; - IMPORTANT: use
bundle idof your RoboVM application.
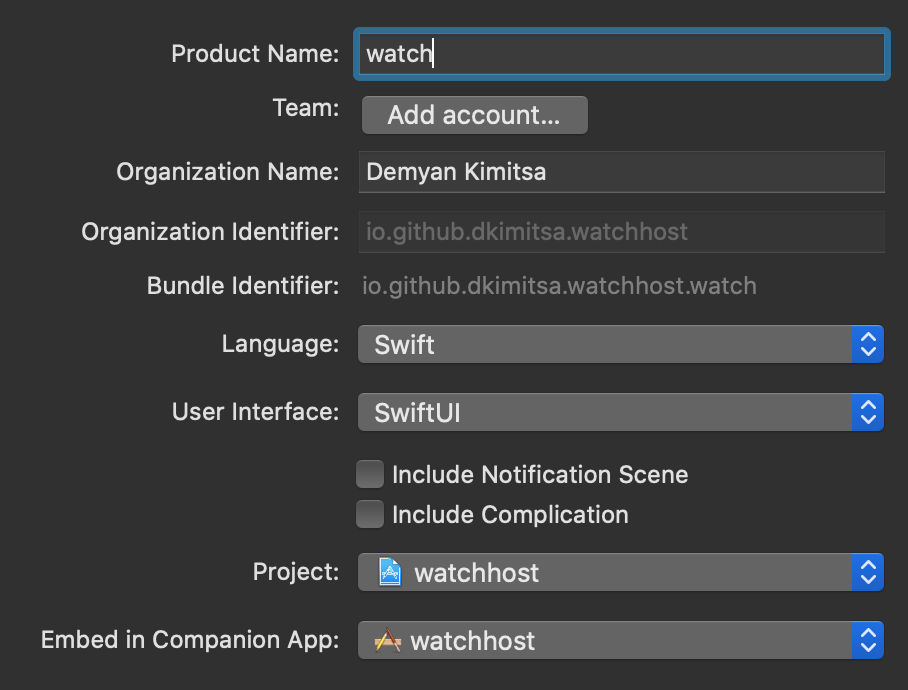
new Xcode dependent watchOS target
- Create new
watchOS/Watch App for iOS Apptarget; - Select
swiftas language; - Select
swiftuias UI; - do not select
Include Notification Scene- to keep project simple; - do not select
Include Complication- to keep project simple; - activate
watchscheme once asked.
Adding functionality
Scope of this tutorial is simple functionality:
- common(similar) UI for both watch/ios with
sendbutton; send/receive counters and text view for logs; - common(similar) Watch Connectivity code to exchange messages;
- watch sends
ping; iphone sendspong.
Watch UI
Replace watch extension/ContentView.swift with following swiftui code:
import SwiftUI
class ExternalModel: ObservableObject {
var me = ""
var other = ""
var sentCnt = 0
var receivedCnt = 0
@Published var buttonTitle: String = ""
@Published var buttonDisabled = false
@Published var sent: String = ""
@Published var received: String = ""
@Published var log: String = ""
init(me: String, other: String) {
self.me = me
self.other = other
buttonTitle = "\(me) it!"
}
func enableButton() -> Void {
buttonTitle = "\(me) it!"
buttonDisabled = false
}
func msgSent() -> Void {
sentCnt += 1;
sent = "\(me) sent: \(sentCnt)"
enableButton()
}
func msgReceived(msg: [String:Any]) -> Void {
receivedCnt += 1
received = "\(other) received: \(receivedCnt)"
log = "\(Date()): Received \(String(describing: msg))"
}
func onError(err: Error?) {
log = "\(Date()): Error \(String(describing: err))"
enableButton()
}
func log(msg: String) {
log = "\(Date()): \(msg)"
}
func onSending() {
buttonTitle = "Wait, sending!"
buttonDisabled = true
log = ""
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var viewModel: ExternalModel
var onClick: (() -> Void) = { }
init(model : ExternalModel, action: @escaping (() -> Void)) {
self.viewModel = model
self.onClick = action
}
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
VStack {
Button(action: onClick) {
Text(self.viewModel.buttonTitle)
.disabled(self.viewModel.buttonDisabled)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, minHeight: 100)
.foregroundColor(Color.black)
.background(Color.yellow)
.padding()
}
Text(self.viewModel.sent)
Text(self.viewModel.received)
Text(self.viewModel.log)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
.fixedSize(horizontal: false, vertical: true)
}
}
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
let model = ExternalModel(me: "Ping", other: "Pong")
model.msgSent()
model.msgReceived(msg: ["msg": "hello"])
return ContentView(model: model, action: {})
}
}
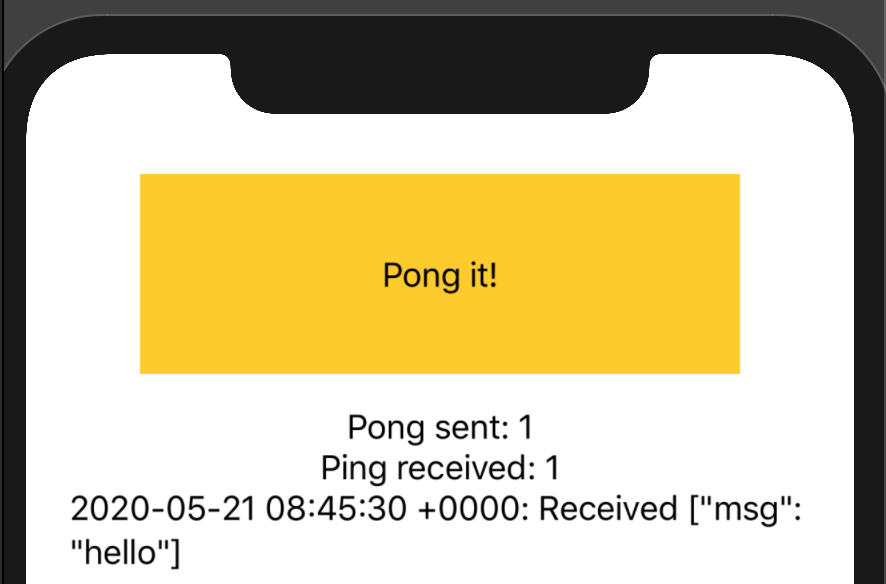
Code above results in following preview:

In code above ExternalModel is used to modify swiftui entries from outside swiftui code, e.g. from communication code, and ContentView implements simple UI described above and picks data from ExternalModel.
Host application UI
Code almost exactly same as in case of watch app.
Replace watchhost/ContentView.swift with following swiftui code:
import SwiftUI
class ExternalModel: ObservableObject {
var me = ""
var other = ""
var sentCnt = 0
var receivedCnt = 0
@Published var buttonTitle: String = ""
@Published var buttonDisabled = false
@Published var sent: String = ""
@Published var received: String = ""
@Published var log: String = ""
init(me: String, other: String) {
self.me = me
self.other = other
buttonTitle = "\(me) it!"
}
func enableButton() -> Void {
buttonTitle = "\(me) it!"
buttonDisabled = false
}
func msgSent() -> Void {
sentCnt += 1;
sent = "\(me) sent: \(sentCnt)"
enableButton()
}
func msgReceived(msg: [String:Any]) -> Void {
receivedCnt += 1
received = "\(other) received: \(receivedCnt)"
log = "\(Date()): Received \(String(describing: msg))"
}
func onError(err: Error?) {
log = "\(Date()): Error \(String(describing: err))"
enableButton()
}
func log(msg: String) {
log = "\(Date()): \(msg)"
}
func onSending() {
buttonTitle = "Wait, sending!"
buttonDisabled = true
log = ""
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var viewModel: ExternalModel
var onClick: (() -> Void) = { }
init(model : ExternalModel, action: @escaping (() -> Void)) {
self.viewModel = model
self.onClick = action
}
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
VStack {
Button(action: onClick) {
Text(self.viewModel.buttonTitle)
.disabled(self.viewModel.buttonDisabled)
.frame(minWidth: 300, minHeight: 100)
.foregroundColor(Color.black)
.background(Color.yellow)
.padding()
}
Text(self.viewModel.sent)
Text(self.viewModel.received)
Text(self.viewModel.log)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
.fixedSize(horizontal: false, vertical: true)
}
}
}
}
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
let model = ExternalModel(me: "Pong", other: "Ping")
model.msgSent()
model.msgReceived(msg: ["msg": "hello"])
return ContentView(model: model, action: {})
}
}
Code above results in following preview:
Adding WatchConnectivity
In scope of tutorial functionality is VERY basic: sending and receiving basic messages.
watch application – WCSessionDelegate
Add SessionDelegate code to watch Extension/ExtensionDelegate.swift:
import WatchConnectivity
class SessionDelegate : NSObject, WCSessionDelegate {
var onMessageReceived : ((_ msg: [String : Any]) -> Void) = { _ in }
var onLog : ((_ msg: String) -> Void) = { _ in}
func session(_ session: WCSession, activationDidCompleteWith activationState: WCSessionActivationState, error: Error?) {
onLog("activationDidCompleteWith activationState = \(activationState) error = \(String(describing: error))")
}
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any]) {
onMessageReceived(message)
}
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any], replyHandler: @escaping ([String : Any]) -> Void) {
onMessageReceived(message)
replyHandler(["msg" : "ok"])
}
}
WCSessionDelegate is very primitive, it just delegates events to lambdas that to be installed externally.
Activate WatchConnectivity in applicationDidFinishLaunching:
let wcSessionDelegate = SessionDelegate()
func applicationDidFinishLaunching() {
// Perform any final initialization of your application.
assert(WCSession.isSupported())
WCSession.default.delegate = wcSessionDelegate
WCSession.default.activate()
}
ios(host) application – WCSessionDelegate
Approach is same to watch application.
Add SessionDelegate code to watchhost/AppDelegate.swift:
import WatchConnectivity
class SessionDelegate : NSObject, WCSessionDelegate {
var onMessageReceived : ((_ msg: [String : Any]) -> Void) = { _ in }
var onLog : ((_ msg: String) -> Void) = { _ in}
func session(_ session: WCSession, activationDidCompleteWith activationState: WCSessionActivationState, error: Error?) {
onLog("activationDidCompleteWith activationState = \(activationState) error = \(String(describing: error))")
}
func sessionDidBecomeInactive(_ session: WCSession) {
onLog("sessionDidBecomeInactive")
}
func sessionDidDeactivate(_ session: WCSession) {
onLog("sessionDidDeactivate")
}
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any]) {
onMessageReceived(message)
}
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any], replyHandler: @escaping ([String : Any]) -> Void) {
onMessageReceived(message)
replyHandler(["msg" : "ok"])
}
}
Also activate WatchConnectivity in applicationDidFinishLaunching:
let wcSessionDelegate = SessionDelegate()
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
// Perform any final initialization of your application.
assert(WCSession.isSupported())
WCSession.default.delegate = wcSessionDelegate
WCSession.default.activate()
return true
}
bringing things together
watch app
Edit watch Extension/HostingController.swift and update body as bellow:
import WatchConnectivity
class HostingController: WKHostingController<ContentView> {
let model = ExternalModel(me: "Ping", other: "Pong")
override var body: ContentView {
// subscribe for message
(WCSession.default.delegate as? SessionDelegate)?.onMessageReceived = { msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.msgReceived(msg: msg)
}
}
(WCSession.default.delegate as? SessionDelegate)?.onLog = { msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.log(msg: msg)
}
}
// action once clicked
let onClickAction = {
self.model.onSending()
WCSession.default.sendMessage(["msg" : self.model.me], replyHandler:{ msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.msgSent()
}
}, errorHandler: { err in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.onError(err: err)
}
})
}
return ContentView(model: model, action: onClickAction)
}
}
What happens here:
- external model is created to connect
SessionDelegatewithswiftui; - once button is clicked in
uimessage is sent usingWCSession.default.sendMessage; - once message or log is received by
SessionDelegateit updatesuithrough model.
ios(host) app
Changes and logic for ios application are similar/same to watch app. Edit watchhost/SceneDelegate.swift and modify willConnectTo as bellow:
import WatchConnectivity
//...
let model = ExternalModel(me: "Pong", other: "Ping")
func scene(_ scene: UIScene, willConnectTo session: UISceneSession, options connectionOptions: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) {
// Use this method to optionally configure and attach the UIWindow `window` to the provided UIWindowScene `scene`.
// If using a storyboard, the `window` property will automatically be initialized and attached to the scene.
// This delegate does not imply the connecting scene or session are new (see `application:configurationForConnectingSceneSession` instead).
// subscribe for message
(WCSession.default.delegate as? SessionDelegate)?.onMessageReceived = { msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.msgReceived(msg: msg)
}
}
(WCSession.default.delegate as? SessionDelegate)?.onLog = { msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.log(msg: msg)
}
}
// action once clicked
let onClickAction = {
self.model.onSending()
WCSession.default.sendMessage(["msg" : self.model.me], replyHandler:{ msg in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.msgSent()
}
}, errorHandler: { err in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.model.onError(err: err)
}
})
}
let contentView = ContentView(model: model, action: onClickAction)
// Use a UIHostingController as window root view controller.
if let windowScene = scene as? UIWindowScene {
let window = UIWindow(windowScene: windowScene)
window.rootViewController = UIHostingController(rootView: contentView)
self.window = window
window.makeKeyAndVisible()
}
}
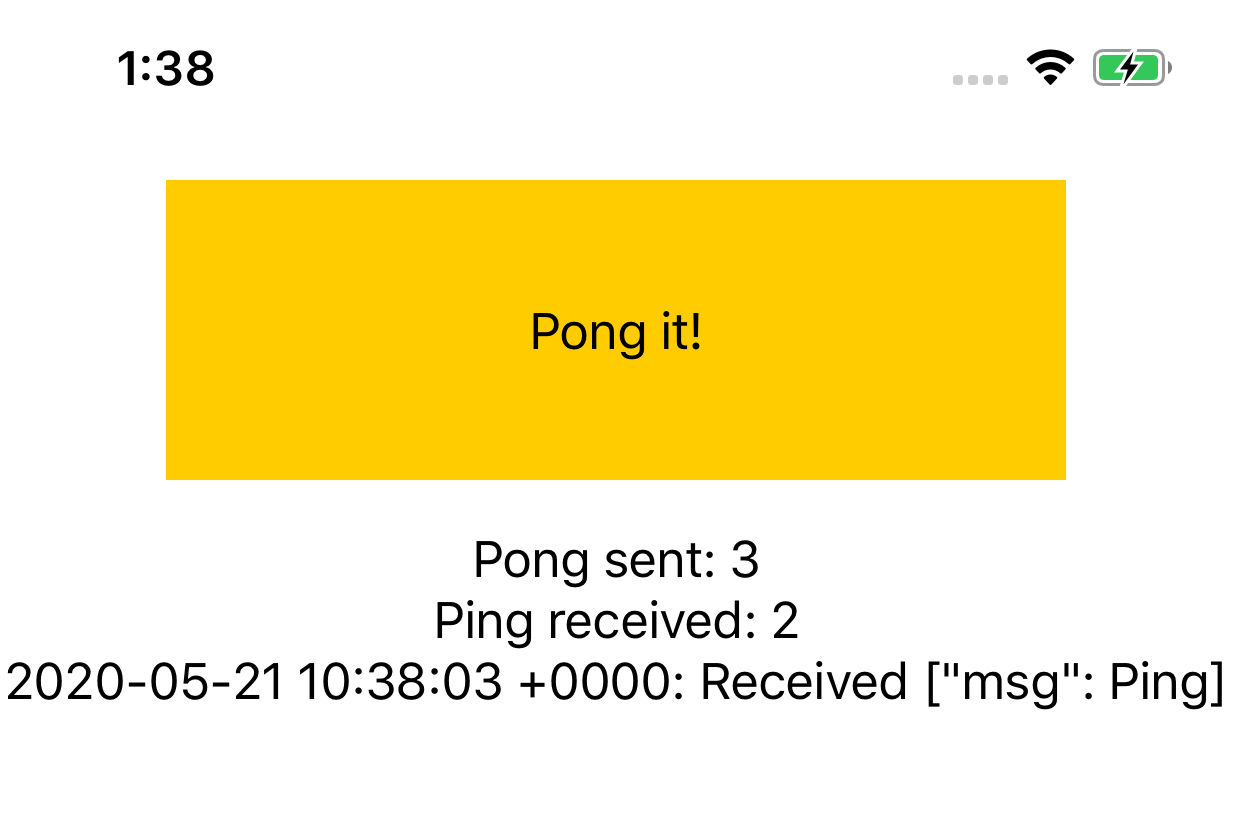
At this moment both ios and watchOS applications should be working and able to send messages each-other:
Watch:
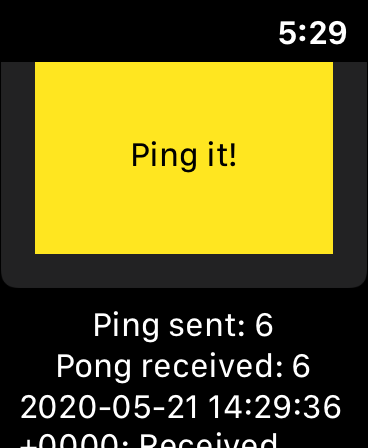
iOS:
RoboVM iOS project
Things are working in native projects, lets port to RoboVM.
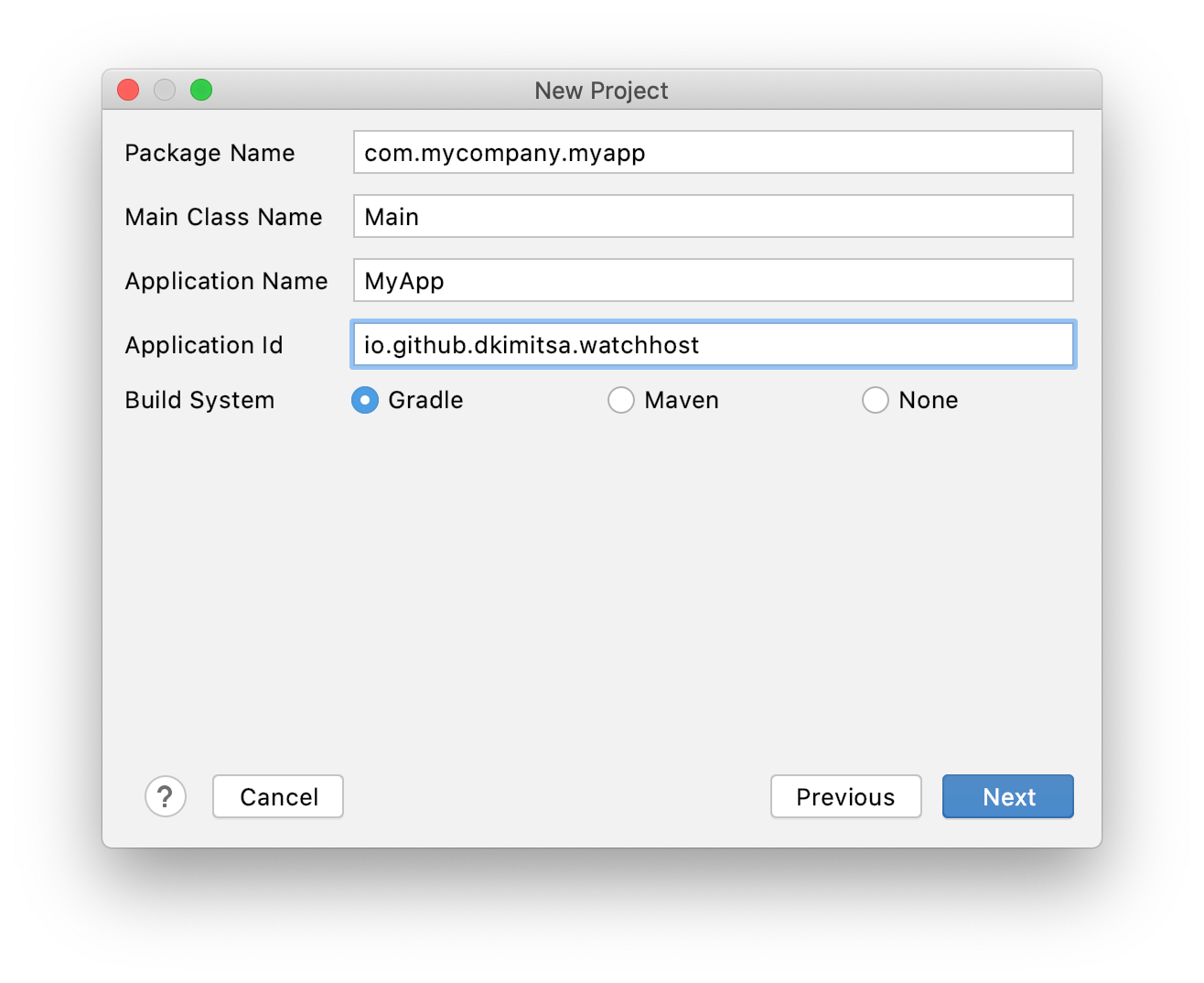
In Intellij IDEA create new RoboVM/RoboVM iOS App without storyboard project. Use gradle build system. Enter same bundle id (io.github.dkimitsa.watchhost) used for native iOS app into Application Id field.
Builing watchOS app binaries
RoboVM app requires pre-build watchOS application. Run xcodebuild command bellow to build watch application for running on a device.
xcodebuild -configuration Release -scheme watch build \
CODE_SIGNING_REQUIRED=NO CODE_SIGNING_ALLOWED=NO \
CONFIGURATION_BUILD_DIR=../robovm-watchapp/exts-dev/
Few notes:
- code signing actively disabled as RoboVM will resign extensions;
CONFIGURATION_BUILD_DIRspecifies dir where to put binaries. Good idea to place it in the directory where RoboVM will be looking for it.
Build for a simulator is a bit tricky as it requires the name of valid simulator to be provided in -destination parameter:
xcodebuild -configuration Release -scheme watch build \
-destination 'name=iPhone 11 Pro' \
CODE_SIGNING_REQUIRED=NO CODE_SIGNING_ALLOWED=NO \
CONFIGURATION_BUILD_DIR=../robovm-watchapp/exts-sim/
Referencing watchOS app in robovm.xml
Following to be added to enable compiler to pickup and pack watchOS application:
<watchKitApp>
<app>watch.app</app>
</watchKitApp>
<appExtensionPaths>
<!-- path where app extensions (such as watch.app) will be searched in -->
<path>exts-sim</path>
</appExtensionPaths>
Porting session delegate
Create new class SessionDelegate and replace its content. Its direct port of the native one:
package com.mycompany.myapp;
import org.robovm.apple.foundation.NSDictionary;
import org.robovm.apple.foundation.NSError;
import org.robovm.apple.foundation.NSString;
import org.robovm.apple.watchconnectivity.WCSession;
import org.robovm.apple.watchconnectivity.WCSessionActivationState;
import org.robovm.apple.watchconnectivity.WCSessionDelegateAdapter;
import org.robovm.objc.block.VoidBlock1;
public class SessionDelegate extends WCSessionDelegateAdapter {
interface Callback<T> {
void invoke(T data);
}
public Callback<NSDictionary<NSString,?>> onMessageReceived = msg -> {};
public Callback<String> onLog = msg -> {};
@Override
public void activationDidComplete(WCSession session, WCSessionActivationState activationState, NSError error) {
onLog.invoke("activationDidCompleteWith activationState = " + activationState +
" error = " + error);
}
@Override
public void sessionDidBecomeInactive(WCSession session) {
onLog.invoke("sessionDidBecomeInactive");
}
@Override
public void sessionDidDeactivate(WCSession session) {
onLog.invoke("sessionDidDeactivate");
}
@Override
public void didReceiveMessage(WCSession session, NSDictionary<NSString, ?> message) {
onMessageReceived.invoke(message);
}
@Override
public void didReceiveMessage(WCSession session, NSDictionary<NSString, ?> message,
VoidBlock1<NSDictionary<NSString, ?>> replyHandler) {
onMessageReceived.invoke(message);
replyHandler.invoke(new NSDictionary<>(new NSString("msg"), new NSString("ok")));
}
}
Register it same way in application delegate(Main.java):
private final SessionDelegate wcSessionDelegate = new SessionDelegate();
@Override
public boolean didFinishLaunching(UIApplication application, UIApplicationLaunchOptions launchOptions) {
if (!WCSession.isSupported())
throw new IllegalStateException("WCSession is not supported");
WCSession.getDefaultSession().setDelegate(wcSessionDelegate);
WCSession.getDefaultSession().activateSession();
// Set up the view controller.
rootViewController = new MyViewController();
// Create a new window at screen size.
window = new UIWindow(UIScreen.getMainScreen().getBounds());
// Set the view controller as the root controller for the window.
window.setRootViewController(rootViewController);
// Make the window visible.
window.makeKeyAndVisible();
return true;
}
Porting UI
Open MyViewController.java class and replace its constructor and fields with the bellow:
private final UIButton button;
private final UILabel sent;
private final UILabel received;
private final UILabel log;
public MyViewController() {
// Get the view of this view controller.
UIView view = getView();
// Setup background.
view.setBackgroundColor(UIColor.white());
double maxX = view.getFrame().getWidth() - 20;
// Setup button.
button = new UIButton(UIButtonType.RoundedRect);
button.setFrame(new CGRect(10, 40, maxX, 40));
button.setBackgroundColor(UIColor.yellow());
view.addSubview(button);
// Setup labels.
sent = new UILabel(new CGRect(10, 90, maxX, 20));
view.addSubview(sent);
received = new UILabel(new CGRect(10, 120, maxX, 20));
view.addSubview(received);
log = new UILabel(new CGRect(10, 150, maxX, 500));
log.setNumberOfLines(0);
view.addSubview(log);
model = new Model();
setupWatchConnectivity();
}
Add model as inner class:
private final Model model;
private class Model {
private final String me = "Pong";
private final String other = "Ping";
private int sentCnt;
private int receivedCnt;
public Model() {
button.setTitle("Wait, sending!", UIControlState.Disabled);
button.setTitle(me + " it!", UIControlState.Normal);
}
void enableButton() {
button.setEnabled(true);
}
void msgSent() {
sentCnt += 1;
sent.setText(me + " sent: " + sentCnt);
enableButton();
}
void msgReceived(NSDictionary<NSString, ? > msg) {
receivedCnt += 1;
received.setText(other + " received: " + receivedCnt);
log.setText(new Date() + ": Received " + msg);
}
void onError(NSError err) {
log.setText(new Date() + ": Error " + err);
enableButton();
}
void log(String msg) {
log.setText(new Date() + ": " + msg);
}
void onSending() {
button.setEnabled(false);
log.setText("");
}
}
Putting things together:
private void setupWatchConnectivity() {
// subscribe for message
((SessionDelegate)WCSession.getDefaultSession().getDelegate()).onMessageReceived = msg ->
DispatchQueue.getMainQueue().async(() -> model.msgReceived(msg));
((SessionDelegate)WCSession.getDefaultSession().getDelegate()).onLog = msg ->
DispatchQueue.getMainQueue().async(() -> model.log(msg));
// action once clicked
button.addOnTouchUpInsideListener((control, event) -> {
model.onSending();
WCSession.getDefaultSession().sendMessage(
new NSDictionary<>(new NSString("msg"), new NSString(model.me)),
msg -> DispatchQueue.getMainQueue().async(model::msgSent),
err -> DispatchQueue.getMainQueue().async(() -> model.onError(err))
);
});
}
Before starting – run configuration
Create run configuration, select simulator that paired with watch and set Launch paired: checkbox as on image bellow:

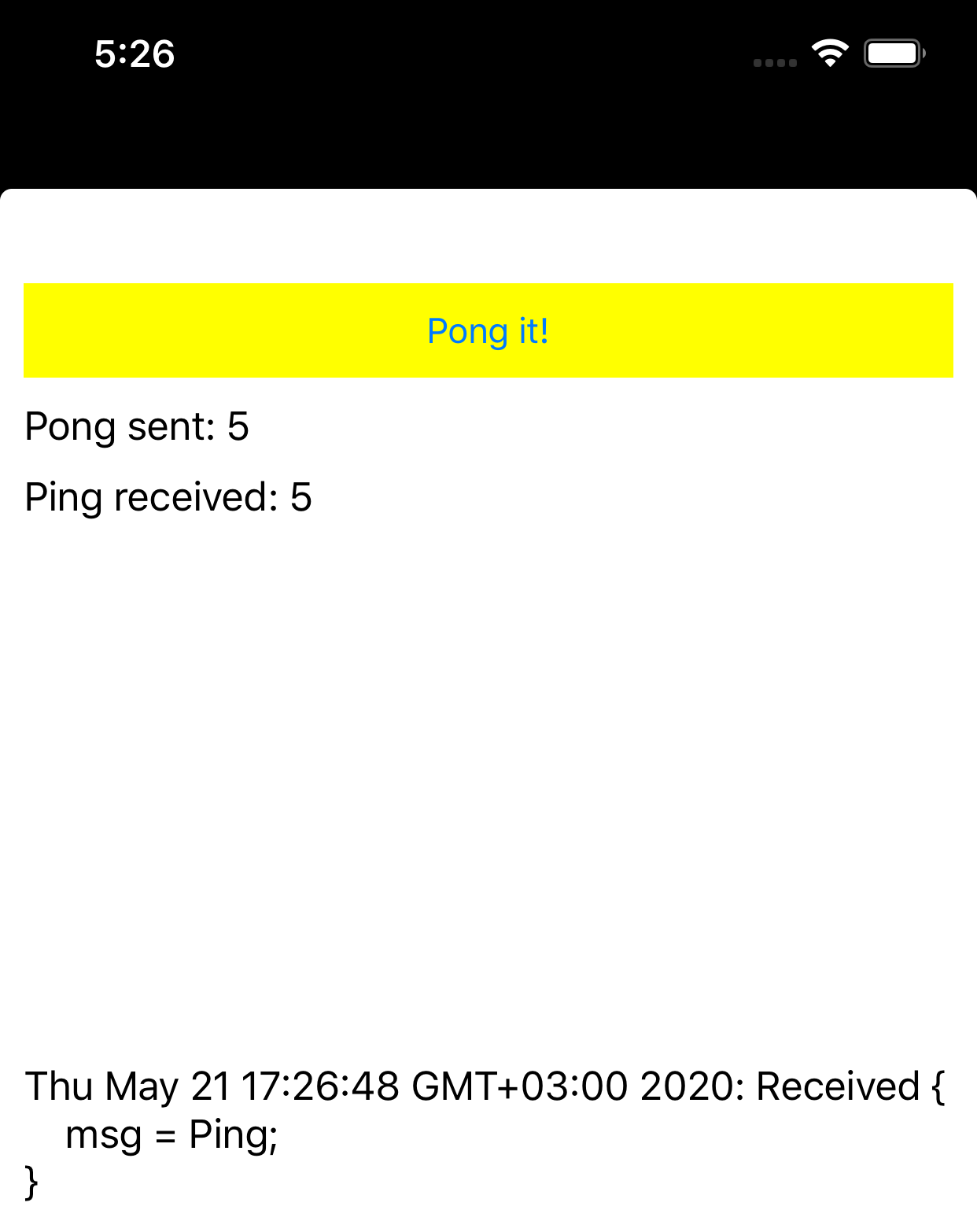
Run
Behaviour is same as in native application. (visual is different due different UI):


Comments